10 Thyroid Symptoms in Females
Thyroid problems in women are more prevalent than in men. While thyroid problems affect approximately 6% of men, the prevalence among women is around 11.4%.
A thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck just under Adam’s apple. Despite its small size, it is crucial in regulating numerous bodily functions, including metabolism, temperature control, and hormone production. When the thyroid gland becomes either overactive or underactive, it can lead to various symptoms and health complications.
In this article, we will explore the various symptoms of thyroid in females and how to know when females should consider getting tested for thyroid issues.
What are the Symptoms of Thyroid in Females?
-
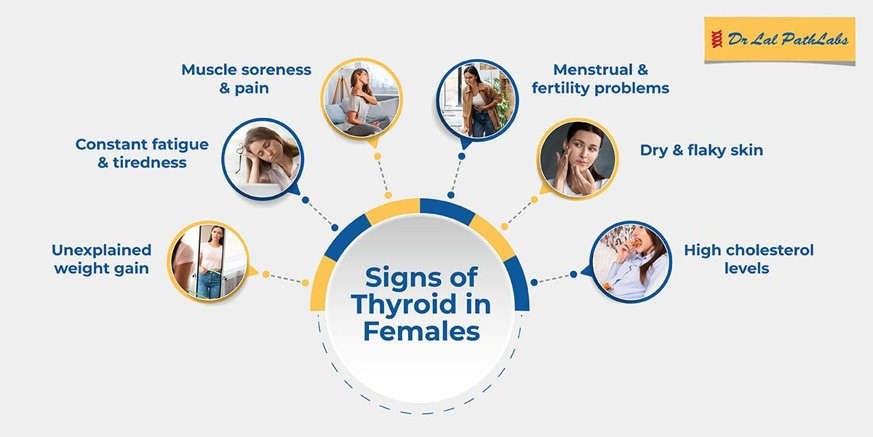
Fatigue and Low Energy
Feeling fatigued even after a good night’s sleep is a common hypothyroidism symptom in females. The thyroid hormones regulate energy production in the body, and low levels can result in persistent fatigue and a lack of energy.
-
Weight Changes
Hypothyroidism often leads to weight gain, even with proper diet and exercise, due to a slowed metabolism. On the other hand, hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) can cause weight loss despite an increased appetite.
-
Mood Swings and Depression
Thyroid hormones influence brain chemistry, and their imbalance can impact mood and emotional well-being. Hypothyroidism is associated with symptoms like depression, irritability, mood swings, and difficulty concentrating. Conversely, hyperthyroidism can cause anxiety, restlessness, and irritability.
-
Hair Loss and Thin/Brittle Hair
Thinning hair, hair loss, and dry, brittle hair are common symptoms of thyroid disease in females. Changes in thyroid hormone levels can disrupt the normal growth cycle of hair follicles, leading to hair problems.
-
Skin Changes
Dry skin, itching, and changes in skin texture are frequently observed in individuals with thyroid issues. Hypothyroidism can lead to dry, rough skin, while hyperthyroidism can cause excessive sweating and moist, warm skin.
-
Menstrual Irregularities
Disruption in the menstrual cycle is another common symptom of thyroid in females. Women with hypothyroidism may experience heavy, prolonged, or irregular periods, while those with hyperthyroidism may have lighter or infrequent periods.
-
Muscle Weakness and Joint Pain
Thyroid dysfunction can lead to muscle weakness, fatigue, and muscle aches. Hypothyroidism, in particular, may cause joint pain and stiffness.
-
Digestive Issues
Another common symptom of thyroid in women is digestive issues. Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can affect digestion. Hypothyroidism can cause constipation, bloating, and a sluggish digestive system, while hyperthyroidism may result in increased bowel movements and diarrhoea.
-
Temperature Sensitivity
Thyroid imbalances can disrupt the body’s temperature regulation. Hypothyroidism symptoms in women often include feeling cold and having a lower body temperature, while hyperthyroidism symptoms in women may include feeling hot and having an increased sensitivity to heat.
-
Changes in Heart Rate and Blood Pressure
An overactive thyroid can accelerate the heart rate, causing palpitations, rapid heartbeat, and high blood pressure. In contrast, an underactive thyroid can lead to a slower heart rate and low blood pressure.
If you are experiencing several of these symptoms or suspect a thyroid disorder, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation. A simple blood test can measure the levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) to determine a thyroid imbalance.
How to Know if You Need a Thyroid Test?
Knowing when a female needs a thyroid test is essential for the early detection and management of thyroid disorders. While it’s best to consult a healthcare professional for personalised advice, here are some typical indications that may suggest the need for a thyroid test:
- Presence of Symptoms: If you are experiencing persistent symptoms associated with thyroid dysfunction, such as unexplained fatigue, weight changes, mood swings, hair loss, menstrual irregularities, or any of the symptoms mentioned earlier, it is worth discussing with your doctor. Be sure to provide a detailed description of your symptoms and their duration.
- Family History: If you have a family history of thyroid disorders, especially in close relatives like parents or siblings, you may have an increased risk of developing a thyroid condition. Informing your doctor about your family history can prompt them to consider a thyroid test as part of your healthcare assessment.
- Age and Gender: Thyroid disorders are more common in women, particularly during specific life stages such as pregnancy, postpartum, perimenopause, and menopause. If you are a female approaching or within these stages and experience any thyroid-related symptoms, it may be appropriate to discuss a thyroid test with your doctor.
- Known Autoimmune Conditions: Autoimmune disorders, such as type 1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, or celiac disease, are more associated with thyroid disorders. If you have a known autoimmune condition, monitoring your thyroid function and discussing the need for testing with your healthcare provider is essential.
- Medication or Treatment Effects: Certain medications or treatments, such as lithium, amiodarone, or radiation therapy to the head or neck, can affect thyroid function. If you are undergoing such treatments or taking medications that impact the thyroid, your doctor may recommend regular thyroid testing to monitor your thyroid function.
- Prior Thyroid Conditions: If you have previously been diagnosed with a thyroid disorder or have had thyroid surgery or radioactive iodine treatment in the past, regular thyroid testing may be necessary to monitor your ongoing thyroid health.
Remember, this list is not exhaustive, and individual circumstances may vary. Therefore consulting with a healthcare professional is essential to determine the need for a thyroid test based on your specific symptoms, medical history, and risk factors.
Final Thoughts
It’s essential for women to be aware of common thyroid symptoms and recognise when a thyroid test may be required to maintain optimal health.
So, if you suspect that you may need a thyroid test, don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider. By taking proactive steps and seeking appropriate medical attention, you can better understand your thyroid health and ensure timely interventions if needed.
Your health is important, and addressing thyroid concerns promptly can lead to improved quality of life and overall wellness.













