Signs, Symptoms, Causes and Treatment of Anemia
Overview
Anemia is a very common medical condition in which the red blood cell count or the hemoglobin in the blood is less than normal. There are various causes of anemia. It could be due to:
- Decreased production of red blood cells in the blood
- Increased blood loss
- Excessive destruction of red blood cells
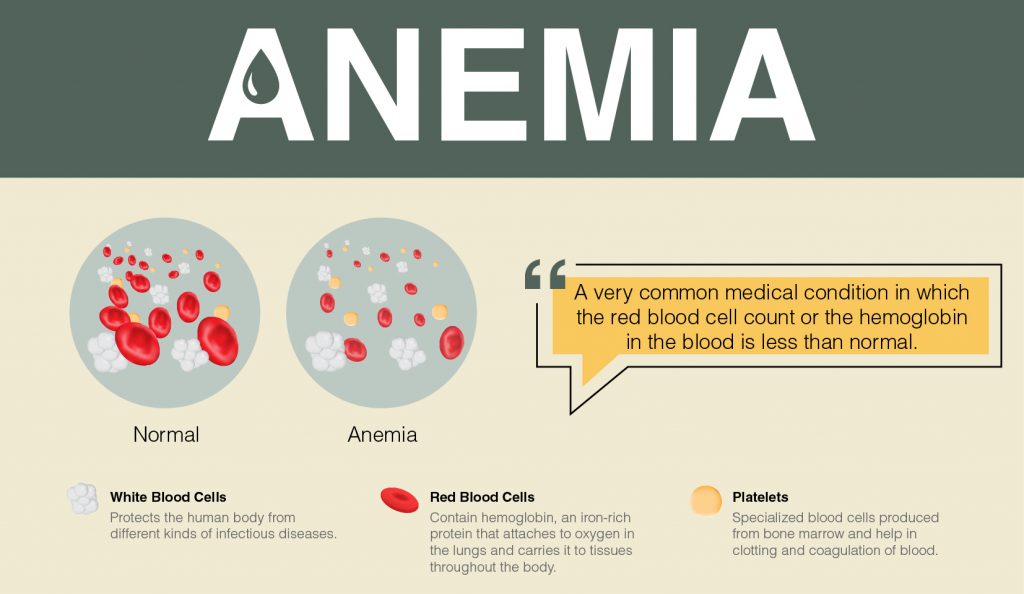
There are mainly three types of cells present in human blood:
- White Blood Cells are involved in protecting the human body from different kinds of infectious diseases.
- Red Blood Cells contain hemoglobin, an iron-rich protein that attaches to oxygen in the lungs and carries it to tissues throughout the body and carries carbon dioxide from other parts of the body to the lungs to be exhaled. The body needs iron, vitamin B-12, folate and other nutrients from the food to produce hemoglobin and red blood cells.
- Platelets are specialized blood cells produced from bone marrow and help in clotting and coagulation of blood.
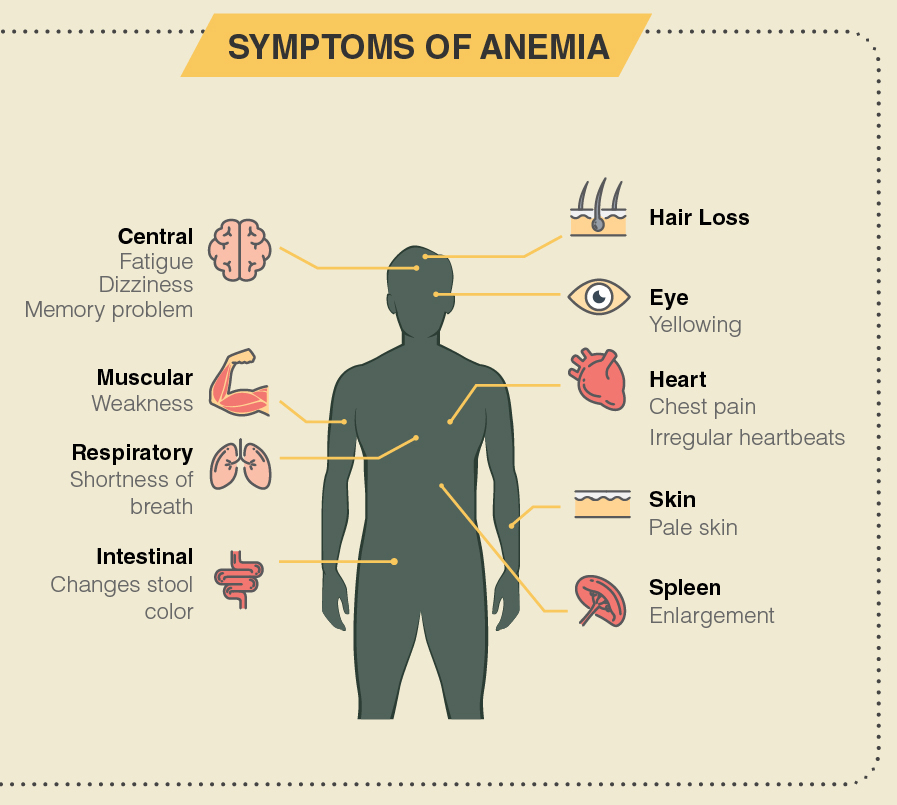
What are the symptoms of Anemia?
Signs and symptoms, if they do occur, might include:
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Cold hands and feet
- Pale skin
- Hair Loss
- Chest pain
- Irregular heartbeats
- Difficulties with memory and concentration
Am I at risk for Anemia?
You may be at increased risk of Anemia in the following cases:
- A diet consistently low in iron, vitamin B-12 and folate
- Intestinal disorders such as Crohn’s disease and celiac disease
- Women of childbearing age are at higher risk for iron-deficiency anemia because of blood loss during their monthly periods.
- Pregnant women are at higher risk for the condition because they need twice as much iron as usual
- Chronic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis or other autoimmune diseases, kidney disease, diabetes, cancer, liver disease, thyroid disease, HIV
- Family history of inherited anemia, such as sickle cell anemia
- People who are over the age of 65 years
- People who face exposure to toxic chemicals
- People who suffer from alcoholism
What are the possible complications of Anemia?
If untreated, anemia can cause many health problems such as:
- Difficulty functioning in everyday life because of fatigue, shortness of breath, and difficulty concentrating
- Pregnancy complications such as premature birth.
- Impaired growth and development in children
- Anemia can lead to a rapid or irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia). In the case of Anemia, the heart has to pump more blood to make up for the lack of oxygen in the blood leading to an enlarged heart or heart failure.
- Some inherited anemias, such as sickle cell anemia, can lead to life-threatening complications.
Tips for preventing Anemia
Iron deficiency anemia and Vitamin deficiency anemia can be avoided by a diet that includes a variety of vitamins and minerals, including:
- Iron: Iron-rich foods include meat, beans, lentils, iron-fortified cereals, dark green leafy vegetables, and dried fruit.
- Folate: It can be found in fruits and fruit juices, dark green leafy vegetables, green peas, kidney beans, peanuts, and enriched grain products, such as bread, cereal, pasta and rice.
- Vitamin B-12: Foods rich in vitamin B-12 include meat, dairy products, and fortified cereal and soy products.
- Vitamin C: Foods rich in vitamin C include citrus fruits and juices, peppers, broccoli, tomatoes, melons and strawberries. These also help increase iron absorption.
How is Anemia treated?
Anemia can be treated, depending upon the causes:
- Iron Deficiency Anemia : Iron deficiency anemia is treated usually by taking iron supplements and changes in diet. If iron deficiency is due to loss of blood (other than menstruation), then the source of blood must be located and treated which might also involve surgery.
- Vitamin Deficiency Anemia : Vitamin deficiencies are treated by involving dietary supplements and increasing nutrients in the diet. In case the body doesn’t absorb Vitamin B-12 from the diet, then additional Vitamin B-12 shots are given.
- Anemia of Chronic Disease : This is anemia associated with a serious, chronic underlying condition. There are no specific treatments, and the focus is on the underlying condition.
- Aplastic Anemia : To boost the red blood cell level, blood transfusion is done as a treatment of Aplastic Anemia. If in case, the bone marrow doesn’t produce healthy blood cells, a bone marrow transplant is done.
- Bone Marrow Disease Anemia : Anemias associated with bone marrow diseases can be treated through several medications, chemotherapy, or bone marrow transplant.
- Hemolytic Anemias : Treatments for hemolytic anemia include blood transfusions, medicines, plasmapheresis, surgery, blood and marrow stem cell transplants, and lifestyle changes.
- Sickle Cell Anemia : Treatment includes oxygen therapy, pain relief, and intravenous fluids. There may also be antibiotics, folic acid supplements, and blood transfusions.
- Thalassemia : In the case of severe Thalassemia, blood transfusion, folic acid supplements, removal of spleen, blood or a bone marrow stem cell transplant is recommended.
Post a Comment












