An Overview of Breast Cancer Test
Overview
Breast cancers are malignant tumors that arise from the uncontrolled growth of cells in the breast. Occurring primarily in the ducts that transport milk to the nipple during lactation (breast feeding), and secondarily in the lobules the glands that produce milk, breast cancers are distinct from cancers that may spread to the breasts from other parts of the body. Laboratory tests for Breast Cancer can be broken down into groups, based on the purpose of
testing:
- To diagnose: cytology ‐ a microscopic examination of tumor cells obtained through fine
needle aspiration and surgical pathology ‐ a microscopic examination of tissue sampling
via biopsy - To determine treatment options: evaluation of the tumor’s HER‐2/ neu gene
amplification status and estrogen and progesterone receptor status - To monitor treatment and for recurrence: measurement of CA 15‐3 or CA 27.29 in the
blood
Why Is It Done?
It is important to remember that most lumps found in the breast are not cancerous but are
benign and that the symptoms and signs associated with breast cancer may be due to other
causes. So to clear all doubts regarding Breast Cancer one should undergo these tests. You
should undergo diagnostic tests for breast cancer if any of the following symptoms come up:
- Mass or lump in the breast
- Breast skin dimpling, reddening, or thickening
- Nipple retraction
- Breast swelling or pain
- Nipple pain and/or discharge
- Swelling or lumps in adjacent underarm lymph node.
How to Prepare?
Some tests for breast cancer are performed on the patient’s blood; others are done on a
sample of cells or the tumour tissue.
For Blood Test: There is no special preparation required for blood test.
For Tissue Test: Your doctor needs to extract the affected tissue so you need to send the same
for testing in the pathology lab.
How it is done?
Blood Test:
The health professional (phlebotomist) drawing blood will:
- Wrap an elastic band (tourniquet) around your upper arm to stop the flow of blood. This makes the veins below the band larger so it is easier to put a needle into the vein.
- Clean the needle site with alcohol.
- Put the needle into the vein. More than one needle stick may be needed. Attach
a tube to the needle to fill it with blood. - Remove the band from your arm when enough blood is collected.
- Apply a gauze pad or cotton ball over the needle site as the needle is removed.
Apply pressure to the site and then a bandage.
Factors Which Affect the Test
As such there is no factor, which affects the test but still before going for the test, you must talk
to your doctor.
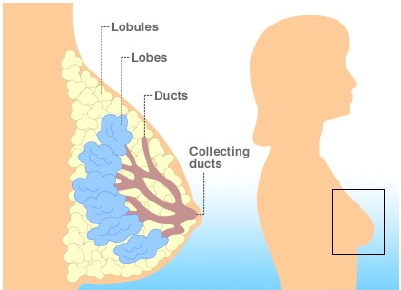
IMAGE: RED AREA SHOWING OCCURRENCE OF BREAST CANCER (X‐RAY IMAGE)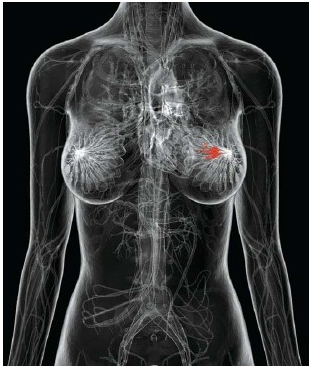 IMAGE: LOBULES AND DUCTS WHERE BREAST CANCER USUALLY OCCURS
IMAGE: LOBULES AND DUCTS WHERE BREAST CANCER USUALLY OCCURS