Anxiety During Pregnancy- Its Treatment and Precautionary Measures
 Changes to the expecting mother’s body are well documented and known across the globe. What needs to be actively discussed is the impact of physical changes on woman’s psychology that causes depression and anxiety during pregnancy. Although each pregnancy is different, there are several bodily changes happen to a woman during this period. Some of them are- swelling of hands, breasts, and other parts of the body, loosening of ligaments accompanied by varicose veins, etc. are quite common during the prenatal period. There are several guidelines that can be followed to stay physically fit and healthy. But none of them focus on keeping psychologically healthy and fit.
Changes to the expecting mother’s body are well documented and known across the globe. What needs to be actively discussed is the impact of physical changes on woman’s psychology that causes depression and anxiety during pregnancy. Although each pregnancy is different, there are several bodily changes happen to a woman during this period. Some of them are- swelling of hands, breasts, and other parts of the body, loosening of ligaments accompanied by varicose veins, etc. are quite common during the prenatal period. There are several guidelines that can be followed to stay physically fit and healthy. But none of them focus on keeping psychologically healthy and fit.
Onset of Depression and Anxiety during pregnancy
Depression is more than just a feeling and is considered to be a serious illness that involves the brain. Depression interferes with our day – to day- lives and is a serious problem during and after pregnancy. Depression and anxiety can be mild, moderate and severe and is the most common complication during and after pregnancy.
How common is depression during pregnancy
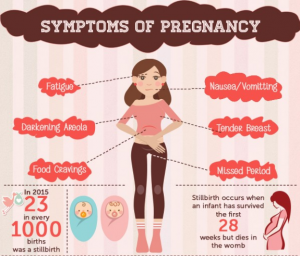
Postpartum anxiety and depression often starts in pregnancy and is characterized by anxiety. Depression and anxiety are considered to be the number one complication of childbirth. Often, they are not recognized, because it shows similar symptom as normal pregnancy has, and all the symptoms happen at the same time like tiredness, sleeping problems, stronger emotional reactions and changes in body weight during and after pregnancy. Similarly, these symptoms can also be the signs of depression.
What causes Anxiety
There are numerous reasons why pregnancy can cause anxiety and depression in women. Some of them are:
- A stressful event such as demise of loved ones,
- History of depression or substance abuse,
- Hormonal factors unique to women may contribute to depression in some women. Hormones immediately affect the brain chemistry that controls emotions and mood. Women are at greater risk of depression at certain times in their lives, such as- puberty, during pregnancy and during premenopause. Some women also suffer from depressive symptoms right before their period. During pregnancy, levels of the female hormones oestrogen and progesterone increase to a great extent.
During the first 24 hours after childbirth, hormone levels quickly return to normal. Researchers think that a significant change in hormone levels may lead to depression.
- Levels of thyroid hormones may also drop immediately after giving birth. Low levels of thyroid hormones because symptoms of depression such as- irritability, mood changes, fatigue anxiety, etc.
- Family history of mental illness, like depression, is a mental illness that tends to run in families
- Problems with previous pregnancy or birth,
- Marital or financial problems
- Changes in the brain chemistry or structure play an important role, leads to depression
Other factors contribute to depression and anxiety during and after pregnancy are:
- Feeling tired after delivery, interrupted sleep patterns and improper rest often keeps away a new mother from regaining her full strength for weeks.
- Feeling stressed from the changes in work and home routines. Sometimes, they want to perfectly manage each and everything by their own, which is not the realistic situation and led to stress.
Any of these above symptoms during and after pregnancy that lasts longer than two weeks are signs of depression:
- Feeling restless or irritable
- Feeling sad, hopeless and overwhelmed
- Crying a lot
- Having less motivation or energy
- Eating and sleeping too little
- Trouble focusing, remembering or making decisions
- Feeling worthless and guilty
- Loss of interest or pleasure in activities.
- Having heavy headaches, chest pains, heart palpitations or hyperventilation (fast and shallow breathing)
Depression after pregnancy: Categories
Mood swings and other changes in a women’s body after pregnancy are classified into three categories- Baby Blues, Postpartum Psychosis, and postpartum depression
- ‘Baby blues’ is a common experience for new mothers during the first few days after pregnancy. In this case, women may feel extremely happy or sad- both with unexplainable crying. However, this experience normally resolves after two to three weeks even without treatments.
- Postpartum psychosis affects one in every 1,000 new mothers. This is the gravest and dangerous types of condition after pregnancy, cause bizarre behaviour, self – neglect, confusion, hallucinations, delusions and illogical thoughts which are often about the new-born. Women with this state of mind require immediate treatments and constant supervision.
- Depression and anxiety during pregnancy, on the other hand, has more severe symptoms than baby blues and affect more women about 15% after childbirth. Unfortunately, these symptoms are not easy to identify because most of its symptoms are similar to the normal changes experienced after pregnancy.
Studies have shown that since long, pregnant women often experience some of the forms of anxiety during as well as post pregnancy that most of the times lead to depression. Pregnancy can put immense pressure on the mental health of a woman. It has been estimated that mental illness affects approximately 20 percent of the women during pregnancy or the first year after giving birth to a baby.
According to the National Institute for Health of a woman, the only instance where the expecting mother will undergo a cognitive screening test is when she has a pre-existing mental illness.
What should one do to if one face symptoms of depression and anxiety during pregnancy?
Some women avoid telling anyone about their symptoms because they feel embarrassed and ashamed about feeling depressed because of the fear being called ‘unfit’ mothers. It has been noticed that women who suffer from anxiety during pregnancy, tend to over think and over analyse the situations that might not need as much as attention. These lead to negative thought, and further women become low on self-esteem. This adds significantly to the risk of post-natal depression. Consulting your doctor or mental health professional who specializes in treating depression is the best option one should opt for.
Here are some other helpful tips:
- Trying to take a nap much as one can ,
- You should stop putting pressure on yourself to do everything and do as much as you can and leave the rest,
- Interacting with your partner, friends and family about how you are feeling,
- You should not spend lot of time alone, go out, and take a regular work
- You can also join support group for women with depression
- Avoid to make life changes decisions that can cause unneeded stress and problems.
Prevention and Treatment
Screening for depression and anxiety during pregnancy is essential. There are several methods of relieving yourself from stress. Primarily there are five common types of treatment for depression:
- Group therapy: Every new mother needs support, and practically it is not always feasible that it will be someone from your family. Therefore you ned to build your network by visiting Antenatal classes, antenatal massage and anti-natal yoga classes, etc. of anti-Some female groups and organizations offer group therapies in helping women with postpartum depression. In this way, they can learn to overcome the signs and symptoms of anxiety during and after pregnancy, and feel better about themselves, their babies, and their lives.
- Talk therapy: This involves, talking to therapists, psychologists or social workers in order to change the thinking of the patient. They try to alter your moods, actions, and thoughts into something positive
- Medicine: some doctors suggest to take antidepressant medication to help release the symptoms and postpartum depression. However, on should consult doctors about the pros and cons of taking anti-depressants when breastfeeding. Doctors could provide the best and most appropriate approach for both you and your baby.
- Rest: If one doesn’t want to take medicines while breastfeeding, she should try to rest, sleep and relax as much as you can.
- Spa or Massage: Although during anxiety and depression, one should not spend time alone, but can treat herself to a spa or massage which can significantly give back the self-esteem she lost during the depression.
- Interaction: Interacting or communicating with the people who give positive solutions. The positive attitude of the partner, as well as other family members towards the mother and her pregnancy, can be extremely helpful in reducing stress and anxiety of the new mothers.
All children deserve the chance to have a healthy mother and all mothers deserve the opportunity to enjoy their life with their children. If one is suffering from the symptoms of depression or anxiety during pregnancy or after having a baby, it is suggested to consult the issues with your partner, family or family doctor as it is a normal part of women’s life.