Dengue – Signs and Symptoms
Overview
Dengue, also known as break bone fever, is a mosquito-borne viral infection and is spread to people through the bite of an infected Aedes species mosquito. Dengue is caused by one of four viral serotypes (closely related viruses), designated DEN-1, DEN-2, DEN-3, and DEN-4.
The best way to prevent dengue is to protect from mosquito bites. Early detection of disease and access to proper medical care lowers fatality rates to below 1%.
What are the symptoms of Dengue?
Common signs and symptoms of dengue usually begin about four to seven days after the initial infection and may last up to 10 days. The symptoms may include:
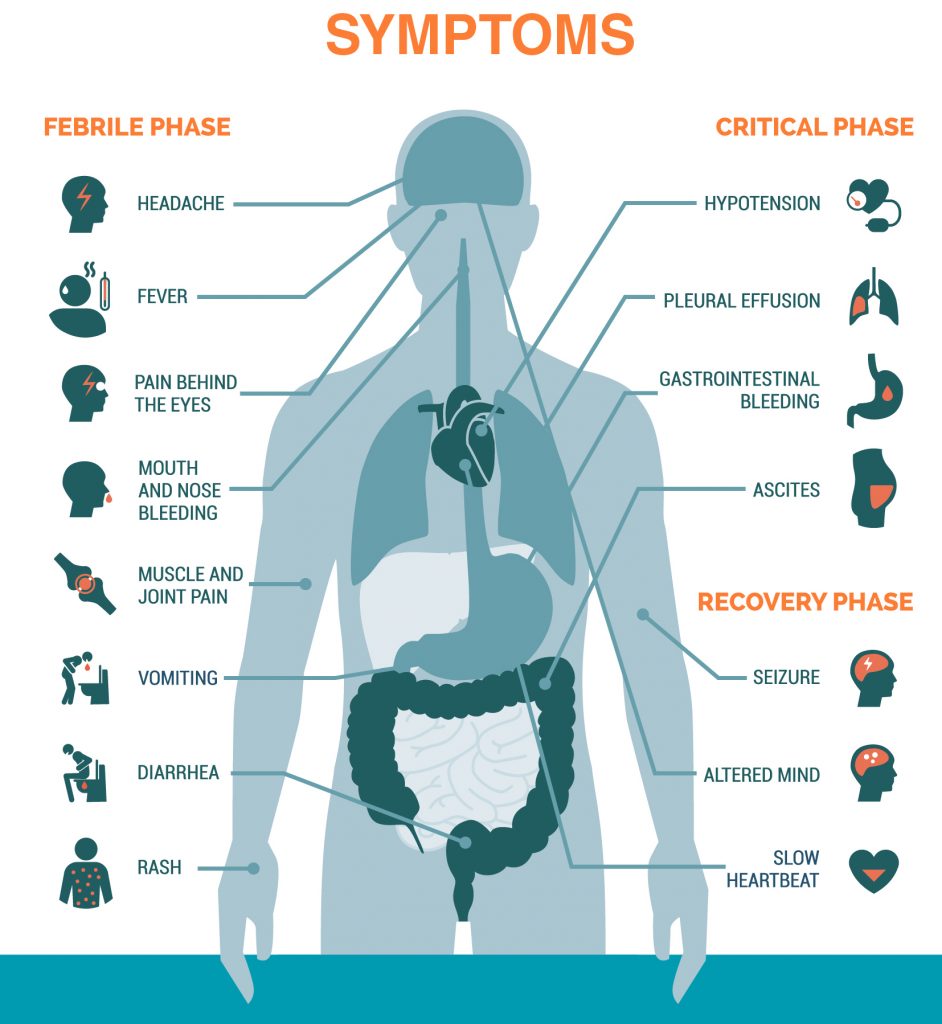
- Headache
- Muscle, bone and joint pain
- High Fever
- Fatigue
- Nausea
- Pain behind the eyes
- Vomiting
- Skin rashes
- Swollen lymph glands
- Mild bleeding, such as bleeding gums or a nose bleed
Signs and symptoms of severe dengue may include:
- Severe abdominal pain
- Persistent vomiting
- Bleeding from gums or nose
- Blood in the urine, stools or vomit
- Rapid breathing
- Irritability or restlessness
- Fatigue
- Clammy skin
- Red spots, particularly on the legs
What causes Dengue?
Dengue fever is caused by any one of four types of dengue viruses spread by mosquitoes. When a mosquito bites a person infected with a dengue virus, the virus enters the mosquito. When the infected mosquito then bites another person, the virus enters that person’s bloodstream.

The probability of developing severe Dengue fever, also known as Dengue Haemorrhagic Fever, increases if a person is infected a second, third or fourth time.
Is dengue dangerous in pregnancy?
A pregnant woman already infected with dengue can pass the virus to her fetus during pregnancy or around the time of birth. Dengue can have harmful effects, including death of the fetus, low birth weight, and premature birth.
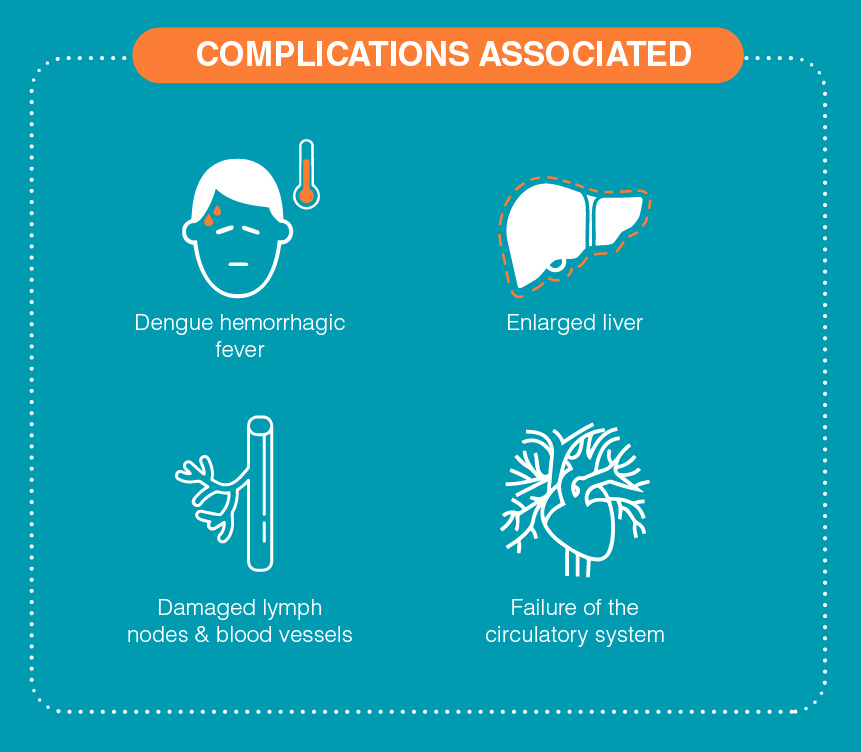
What are the complications associated with Dengue?
A small percentage of people suffering from dengue fever can develop a more serious form of the disease known as dengue hemorrhagic fever. The dengue hemorrhagic fever can trigger dengue shock syndrome. Dengue shock syndrome is severe and can lead to excessive bleeding and even death. The risk factors for developing dengue hemorrhagic fever include:
- Having antibodies to dengue virus from a previous infection
- Being under the age of 12
- Being female
- Weakened immune system
Dengue fever has dangerous effects on the body if left untreated. It can potentially cause the liver to become enlarged or damage the lymph nodes and blood vessels. It can also lead to a failure of the circulatory system and a risk of massive bleeding.
What are the tips for preventing Dengue?
There are no vaccines against dengue fever. The only way of preventing dengue is to avoid mosquito bites. Following steps can be taken to prevent mosquito bites:

- Stay in air-conditioned or well-screened housing
- Wear protective clothing that covers the arms, legs, and head especially when visiting mosquito-infested areas
- Apply insect repellent to skin. The most effective repellents are those containing diethyltoluamide (DEET)
- Apply permethrin insecticide to clothes
- Use mosquito nets impregnated with permethrin
- Cover strollers and baby carriers with mosquito netting
- Reduce mosquito habitat such as standing water that can collect in things such as
- Used automobile tires.
- Pet dishes
- Empty planters
- Flower pots
- Cans
- Any empty vessel
How is Dengue treated?
There is no specific treatment of Dengue fever. Timely intervention can help, depending on how severe the disease is. Here are a few basic treatments of Dengue fever:

- The doctor may generally recommend medications regulating the pain and fever
- Drink plenty of water to avoid dehydration
- Take proper bed rest especially during the days when the fever is at its peak












