The Role of Genetic Testing in Lung Cancer Treatment
- 27 Jan, 2025
- Written by Team Dr Lal PathLabs
Medically Approved by Dr. Seema
Table of Contents

Lung cancer is one of the most prevalent and deadliest forms of cancer the world over and accounts for a number of cancer-related deaths each year. Despite advancements in medical technology and treatment protocols, the prognosis for lung cancer patients often remains poor due to late diagnosis and the disease’s aggressive nature. Genetic testing has revolutionised the approach to lung cancer treatment, enabling personalised therapies targeting specific genetic mutations within cancer cells. This customised approach improves the effectiveness of treatments and reduces unnecessary side effects, improving patients’ overall quality of life.
What Is Lung Cancer?
Lung cancer is a condition characterised by the uncontrolled and rapid growth of abnormal cells in one or both lungs. These abnormal cells fail to carry out the functions of normal lung cells and can cause tumours that interfere with the lungs’ capability to supply oxygen to the bloodstream. The progression of lung cancer is categorised into different stages of lung cancer, ranging from Stage I (localised cancer) to Stage IV (cancer that has spread to other parts of the body).
Genetic lung cancer refers to lung cancers that are driven by specific genetic mutations. These mutations can influence how the cancer behaves and how it responds to certain treatments.
Role of Genetic Testing in Lung Cancer
Genetic testing for cancer has become an integral part of modern oncology, particularly in the management of lung cancer treatment. In patients with non-small cell lung cancer, genetic testing is used to identify specific mutations within the cancer cells. This information is critical in selecting targeted therapies that are more likely to be effective.
Genetic cancer screening helps in detecting mutations in genes such as EGFR, KRAS, and ALK, which are commonly associated with lung cancer:
1. EGFR Mutations: The EGFR gene provides instructions for making a protein that prompts cell growth and division. Mutations in this gene result in cells growing exponentially. Targeted therapies known as EGFR inhibitors can block these signals, slowing or stopping cancer growth.
2. KRAS Mutations: The KRAS gene is involved in regulating cell division. Mutations here can make cancer cells resistant to certain treatments. Knowing if a tumour has a KRAS mutation can help doctors decide which treatments are less likely to be effective.
3. ALK Gene Rearrangements: The ALK gene can fuse with other genes, creating an abnormal gene that promotes cancer development. ALK inhibitors are drugs designed to target this specific mutation, offering a significant therapeutic benefit.
Genetic information about the tumour can also help predict the chances that the lung cancer will return after surgery. This prognostic information is invaluable in making informed decisions about additional treatments, such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy, to bring down the risk of recurrence.
Common Tests for Genetic Lung Cancer
Cancer and genetic testing involve various laboratory tests that analyse tumour samples to detect genetic mutations. These tests are essential in developing a personalised treatment plan for patients.
1. Lung Cancer Test for EGFR and KRAS Mutations
Testing for EGFR and KRAS mutations typically involves collecting a tissue sample from the tumour through a biopsy. The sample is then analysed using molecular testing methods to detect the presence of mutations. Identifying these mutations allows doctors to prescribe targeted therapies that specifically inhibit the mutated proteins.
2. Lung Cancer Screening for Rearrangement of the ALK Gene
For ALK gene rearrangements, fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH) or next-generation sequencing (NGS) techniques are commonly used. Detecting an ALK rearrangement means that patients may benefit from ALK inhibitor drugs, which have been shown to improve survival rates.
3. Testing for Squamous Cell Lung Cancer Mutations
Although genetic mutations are less common in squamous cell carcinoma, testing can reveal alterations in genes such as FGFR1 and DDR2. Clinical trials are exploring targeted therapies against these mutations, providing hope for more effective treatments in the future.
Like with any form of cancer, early diagnosis and treatment lead to better outcomes in lung cancer. Incorporating genetic testing into the diagnostic and treatment process allows for a more personalised approach. For better genetic lung cancer treatment outcomes, consult with a healthcare professional and book a test with Dr Lal PathLabs today.
FAQs
What are the causes of lung cancer?
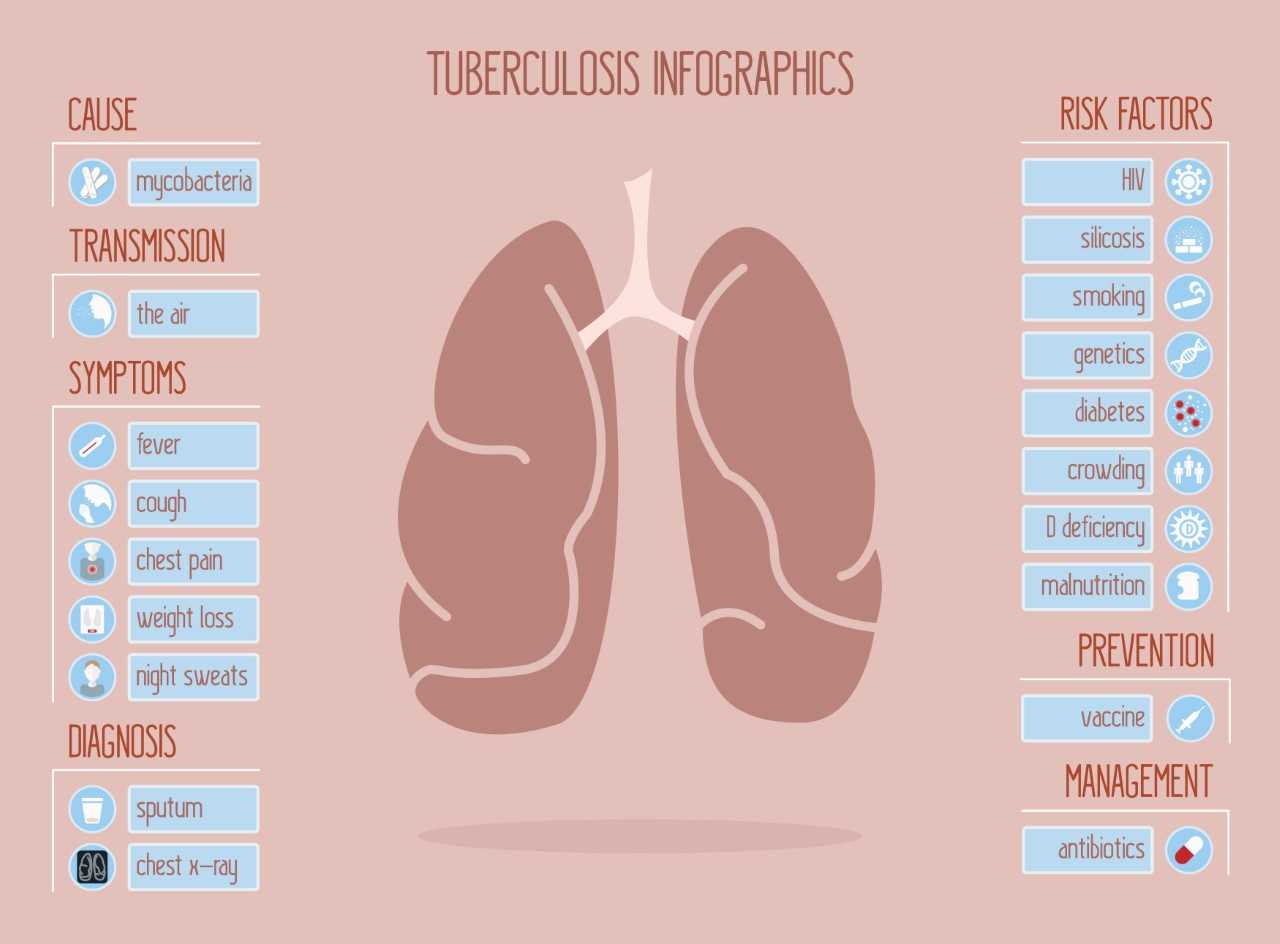
The primary cause of lung cancer is smoking tobacco, which is responsible for about 85% of cases. Other major causes include exposure to radon gas, asbestos, air pollution, and genetic predisposition.
What are the major lung cancer symptoms?
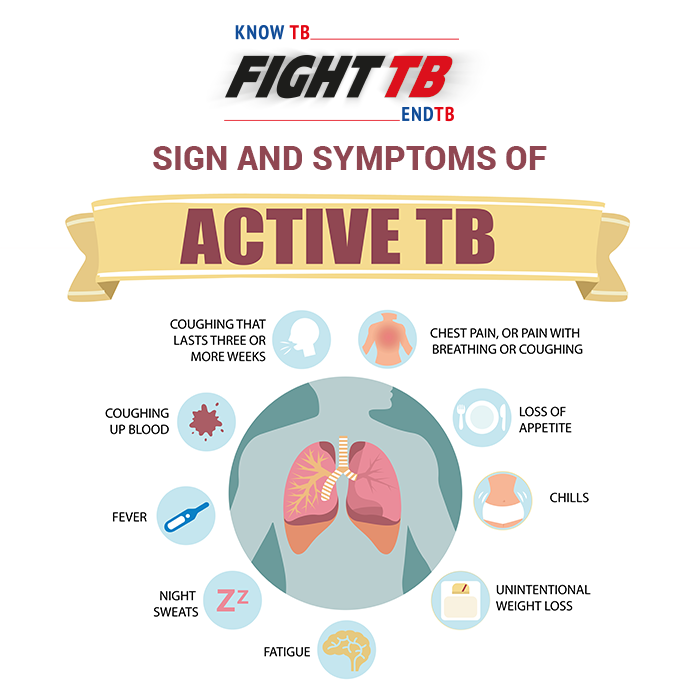
Lung cancer symptoms can manifest in various ways, including a cough that doesn’t go away, discomfort in the chest, difficulty breathing, wheezing, unexpected weight loss, and blood in the sputum. Early stages may not present noticeable symptoms, emphasising the importance of regular lung cancer screening.
When is lung cancer awareness month?
November is designated as Lung Cancer Awareness Month. It aims to increase public awareness about the disease, promote early detection, and support research efforts to improve treatments and outcomes.