Essential Diagnostic Tests for Detecting Rheumatoid Arthritis
- 9 May, 2025
- Written by Team Dr Lal PathLabs
Medically Approved by Dr. Seema
Table of Contents

Rheumatoid Arthritis is an ongoing autoimmune disease that can cause limited mobility and deformed joints. Awareness of this condition is essential because, if left untreated, it may cause further health complications, such as heart disease and osteoporosis.
This article serves as a guide on Rheumatoid Arthritis, including the essential diagnostic tests used for Rheumatoid Arthritis.
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease which affects the joints on both sides of the body. RA commonly targets joints in the knees, wrists, fingers, toes, etc. RA attacks the lining of the joints, which can lead to inflammation and, over time, may erode the bones and damage the joints.
Besides the joints, Rheumatoid Arthritis may affect other parts of the body, such as the skin, lungs, heart, eyes, and mouth.
What are the Types of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
The symptoms and risk of complications may vary across the different types of Rheumatoid Arthritis. There are three RA types:
- Seropositive Rheumatoid Arthritis: It is the most common type of RA. Individuals who test positive for the antibodies rheumatoid factor (RF) as well as anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody (ACPA) are diagnosed with Seropositive RA. They experience more severe symptoms and quicker disease progression.
- Seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis: Individuals who test negative for RF and ACPA may be diagnosed with Seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis. These individuals may experience milder symptoms and respond better to RA treatment.
- Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis is the most common type of arthritis found in children. It shares many of the same symptoms as RA but often has an unknown cause.
What are the Risk Factors of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Certain demographics are at higher risk of developing Rheumatoid Arthritis. The following factors put individuals at greater risk of developing RA:
- Being of the female sex
- Being middle-aged or older
- Being overweight
- Having a family history of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Having a regular smoking habit
What are the Causes of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Unlike the usual immune response that targets harmful agents in the body, the immune system of an RA-affected individual attacks healthy joint tissues instead.
Healthcare professionals do not know the exact Rheumatoid Arthritis causes yet. It may be caused by a combination of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors.
Certain factors, such as smoking and gender, do increase the chances of developing RA. Genetics is also a likely contributing factor.
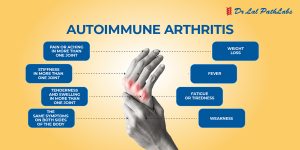
What are the Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Different people develop Rheumatoid Arthritis symptoms at different rates. The most common symptoms include:
- Limited mobility
- Pain or stiffness in multiple joints
- Swelling or tenderness in joints
- Joint pain and stiffness on both sides of the body
- Joint stiffness, particularly in the morning or after long periods of sitting
- Fatigue
- Fever
What are the Diagnostic Tests for RA?
The following are the essential Rheumatoid Arthritis tests commonly used by doctors to detect RA:
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) Test: An ESR test evaluates the extent of inflammation in the body. Higher ESR results indicate greater inflammation and greater chances of RA.
- C-Reactive Protein (CRP) Test: A CRP test evaluates the CRP protein levels present in the bloodstream. CRP is released from the liver when there is an infection and can cause inflammation. Autoimmune conditions like RA can cause high CRP levels in the blood.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): A complete blood count evaluates the cells in the blood, including red and white blood cells and platelets. Rheumatoid Arthritis does not usually affect the blood cells. Thus, abnormal CBC results can help prevent an RA misdiagnosis.
- Rheumatoid Factor Test: An important test for RA, it measures the body’s level of rheumatoid factor protein, a kind of immune system protein that targets the body’s healthy tissues. High levels of rheumatoid factors may indicate Rheumatoid Arthritis.
- Cyclical Citrullinated Peptide (CCP) Antibodies Test: CCP antibodies are proteins that attack the body’s healthy tissues and blood cells. A CCP test measures the presence of CCP antibodies and can also help determine the severity of RA. It is usually performed in conjunction with a Rheumatoid Factor test.
Additionally, healthcare professionals may perform extra tests such as physical assessments, joint scans, and imaging tests.
Diagnosing RA early can help prevent more severe symptoms and provide pain relief sooner. Upon noticing signs of Rheumatoid Arthritis, book a Rheumatoid arthritis test at Dr Lal PathLabs immediately.
FAQs
-
Which age is most likely to develop Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Rheumatoid Arthritis affects people of all ages. However, it most commonly starts developing between the ages of thirty and sixty.
-
Can Rheumatoid Arthritis cause other complications?
If Rheumatoid Arthritis is not treated, it may cause further health complications, including deformed joints, carpal tunnel syndrome, osteoporosis, and heart disease.
-
Does Rheumatoid Arthritis have a cure?
There is no cure for Rheumatoid Arthritis yet. However, various relief methods, including medications, physical therapy, and surgeries, exist that can help reduce the swelling and pain affecting individuals with RA.