BRCA1 and BRCA2: What You Need to Know About Breast Cancer Genes
- 26 Jul, 2025
- Written by Team Dr Lal PathLabs
Medically Approved by Dr. Shuchi
Table of Contents

Certain genes in the cells of the human body are responsible for repairing damaged DNA and maintaining healthy cell growth. Random changes or mutations in such genes can significantly raise the risk of developing cancers. Among the most important of these are BRCA1 and BRCA2, which play a critical role in preventing breast and ovarian cancers.
Individuals with a BRCA mutation may not only face an increased risk of breast cancer but also of ovarian, pancreatic, and prostate cancers. This article explores what BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are and their significance.
What Is BRCA1 and BRCA2?
To understand the inherited risk of cancer, it is important first to know what BRCA1 and BRCA2 are. BRCA, short for Breast Cancer genes, are genes that produce proteins which repair damaged DNA, and their gene products play a significant role in tumor suppression and maintaining genetic stability.
When either BRCA1 (Breast Cancer gene 1) or BRCA2 (Breast Cancer gene 2) is mutated, their DNA repair function is disrupted, which leads to uncontrolled cell growth, resulting in cancer. Mutations in these genes are passed down through either one or both parents in families and are thus present in all cells of the body since birth.
When Is BRCA Testing Done?
Doctors recommend BRCA1 and BRCA2 tests while testing individuals with certain risk factors. These risk factors include:
- A personal or family history of breast cancer.
- A known history of ovarian, fallopian tube, or peritoneal cancer in close relatives.
- History of male breast cancer in the family.
- A known BRCA mutation in a close relative.
- Multiple family members diagnosed with ovarian, pancreatic, or prostate cancer.
- Individuals from specific ethnic groups with higher mutation rates.
BRCA testing can also help establish follow-up treatment plans for patients already diagnosed with breast cancer.
Why Is BRCA Testing Important?
BRCA testing helps assess inherited cancer risk and guide clinical decisions for both patients and their family members. Such a mutation can be used to identify:
- Breast Cancer Risk: Individuals with BRCA mutations have a higher chance of developing breast cancer. Recent research in Springer Open found that almost 29% of Indian breast cancer patients also had BRCA mutations.
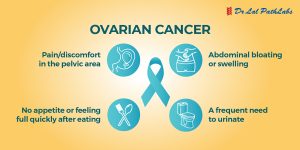
- Ovarian Cancer Risk: Presence of BRCA mutations in women can also indicate a risk of ovarian cancer in them. According to a study published in the National Library of Medicine, that tested some Indian ovarian cancer patients, 15.5% of the patients had BRCA1 mutations, while 5.9% showed BRCA2 mutations.
- Other Cancers: BRCA mutations are also linked to a higher risk of pancreatic cancer, prostate cancer (in men), and melanoma in some cases.
- Follow-up Treatments: Patients with BRCA mutations may be advised to undergo specific follow-up treatments after a thorough consultation with a doctor.
How Is the BRCA Test Performed?
The BRCA1 and BRCA2 tests are genetic tests performed using a blood or saliva sample. It detects harmful changes or mutations in these genes. Here’s how these tests are performed:
- Sample Collection: A standard blood sample or a cheek swab is collected.
- Analysis: DNA is checked for known BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations.
- Reporting: Results generally fall into three categories based on the presence or absence of these mutations.
- Genetic counselling: Pre- and post-test counselling is typically recommended to understand the implications of the results.
How to Interpret BRCA Test Results?
Understanding BRCA test results is essential for making informed decisions. Here’s what different outcomes may indicate:
- Positive Result: Indicates a higher risk of developing breast, ovarian, and other cancers.
- Negative Result: Indicates no BRCA mutation was identified.
- Variants of Uncertain Significance (VUS) Result: Means a genetic change has been detected, but its connection to cancer remains unclear. Further research or follow-up may be necessary.
Results should always be discussed with a medical geneticist or oncologist to determine the next steps.
How Can BRCA-Related Cancer Risk Be Managed?
Managing BRCA-related cancer risk involves a combination of regular monitoring and preventive strategies, all under medical supervision. These include:
- Enhanced screening
- Lifestyle modifications
- Risk-reducing surgeries
- Routine medications
- Family testing
Carrying a BRCA gene mutation enhances the risk of certain cancers. However, with the right combination of medical guidance and proactive strategies, individuals can take meaningful steps to manage their risk.
Individuals with risk factors of BRCA genes are advised to consult their healthcare provider and book a BRCA test with Dr Lal PathLabs. Download the Dr Lal PathLabs app to schedule the test quickly.
FAQs
1. What cancers are linked to BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations?
Mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 can increase the chances of certain cancers, including breast cancer, ovarian, prostate, and pancreatic cancers.
2. Can men carry BRCA mutations?
Yes, men can inherit BRCA mutations and may face increased risks of prostate and breast cancer.