The Crucial Role of Genetics in Detecting Cancer
- 21 Apr, 2025
- Written by Team Dr Lal PathLabs
Medically Approved by Dr. Seema
Table of Contents

Cancer is one of the leading causes of death across the globe, and according to the World Health Organisation, it accounts for around 9.6 million deaths. In India, studies from the Indian Journal of Medical Research found that the estimated cancer cases in India in 2022 were around 1,461,427, suggesting that around 1 in 9 people in the country can develop cancer in their lifetimes.
This number is expected to increase by 12.8% by 2025. Early detection and diagnosis are vital for success when it comes to treatment. In this article, we discuss the role of genetics in detecting cancer.
What is Cancer?
Cancer is a disease that could affect any organ or tissue in the body. Cells in tissues or organs grow abnormally, extending beyond their usual boundaries and invading other body parts. Different genes typically regulate the growth and division of cells.
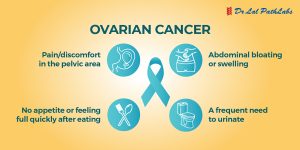
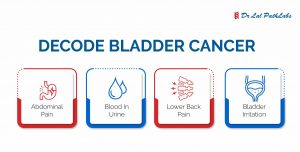
However, specific genetic changes sometimes occur within cells, causing them to become atypical, form tumours, and develop into cancer. The most common forms of this condition are lung, prostate, stomach, liver, breast, cervical, thyroid, and colorectal.
Is Cancer an Inherited or Environmental Condition?
Cancer is a genetic condition and is caused by damaged and mutated DNA. Several factors could lead to these mutations, including:
- Environmental Factors: Carcinogens (agents that cause cancer), such as certain chemicals, UV, tobacco, and radiation exposure, can damage DNA.
- Metabolism: The body’s metabolism refers to converting food into energy for the body’s cells. This process can sometimes cause the cells to damage their DNA, which accumulates over time.
- Spontaneous Mutations: Cells often divide and multiply, and DNA strictly regulates this process. However, spontaneous mutations can occur in some cases.
Genetic mutations do not usually cause negative changes; the body catches and corrects most. However, mutations in specific types of genes can cause cancer.
Is Genetics in Cancer Detection Important?
Genetics play a vital role in cancer detection and assessing for cancer risks. Genetic cancer tests check for any genetic mutations in the DNA. Medical professionals test a small amount of bodily fluids, like blood or saliva. The majority of cancer-causing mutations are not hereditary.
Only 5-10% of all cancers have genetic mutations that may be inherited from a biological parent. Most gene mutations occur after birth. Several factors, including smoking, viruses, radiation, carcinogens, hormones, unhealthy lifestyles, and chronic inflammation, could cause these.
Who Should Get Genetic Testing for Cancer?
Healthcare professionals primarily suggest genetic cancer tests for those who:
- Have a strong family or personal history of cancer or mutations that could cause cancer
- Have or have had several different types of cancer
- Were diagnosed at a young age with cancer
- Have rare cancers
- Develop cancer in a pair of organs, such as both kidneys or breasts
- Have specific symptoms linked to inherited cancer conditions
- Are part of an ethnic or racial group prone to certain inherited cancers
It can be difficult to collect and determine the medical histories of more distant relatives. However, in most instances, medical professionals only require the histories of ‘first-degree relatives’, such as biological siblings or parents. Further testing is recommended if distant relatives have a history of cancer.
If an individual has a family history of cancer or is displaying cancer symptoms, it is necessary to consult a healthcare provider at the earliest.
How Do Genetic Cancer Tests Work?
There are many different types of genetic tests. Depending on the lab and type of test, these may include:
- Blood Samples: A healthcare professional takes a blood sample by inserting a needle inside a vein in the patient’s arm.
- Cheek Swabs: Some genetic tests may require a swab of saliva from the inside of the cheek for testing.
- Skin Cells: Some genetic tests take skin cell samples for testing.
These tests check for specific mutations in the genes or proteins in the cells. They are also helpful for individuals already battling cancer, as they can be used to identify the right treatments and procedures.
While genetic testing is usually accurate, it is not always reliable. An individual may have a positive test result for some gene variants.
It is important to note that having cancer-related mutations does not necessarily indicate that an individual will develop cancer. Having test results examined by a medical professional is crucial for further steps, diagnosis, and treatment.
For efficient and accurate genetic cancer test panels, book a test at Dr Lal PathLabs website today.
FAQs
-
How do you test for genetic cancer?
Cancer gene panels usually require a blood, skin cell, or saliva sample. These are tested for specific genes associated with different cancers.
-
Is it safe to do genetic testing?
Most genetic tests have minimal physical risks, especially blood and cheek swabs.